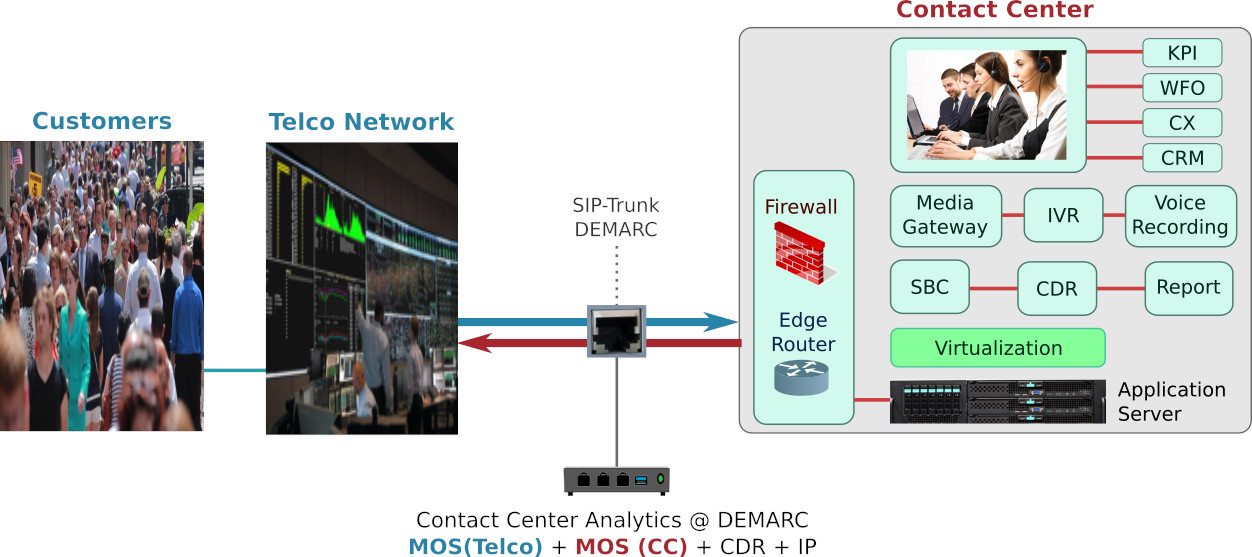
Is Telco or contact centre side causing the problems experienced by customers?
Telco Demarcation point (DEMARC) is where Telco and contact centre (CC) connects, it is also the point where Telco and CC problems can be analyzed independently from each other. MOS score is commonly used to identify Telco side problems, however a low MOS from the CC side indicates there are performance issues with the CC.
Factors, such as codec selection, can change MOS. We focus on the factors that are dynamically linked to CC performance and are measurable for all calls in real-time, even during hours with thousands of calls.
- IP Packet lost is primarily caused by Ethernet buffer overflow inside CC infrastructure.
- Jitter is the variation in the latency on a packet flow through DEMARC from CC, only RTP packets with consecutive sequence number are used for calculation.
- Latency is the time between call-connect and 1st RTP packet flow, it is linked to the speed of call processing during busy hours .
- RTP port error happens when a RTP port is re-assigned prematurely to another call during conversation. When this happens, MOS will be reset to 0 and caller will experience a “dropped-call”.
The following MOS example is based on a real call using G.711/PCMU, please refer to RFC 3551, ITU-T G.107 and ITU-T P.863.1 for more details.

